Set Permissions for a Role
Tenable Identity Exposure uses Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to secure access to its data. A role determines what type of information users can access depending on their functional roles in the organization. When you create a new user in Tenable Identity Exposure, you assign that user a specific role with its associated permissions.
To set permissions for a role:
-
In Tenable Identity Exposure, click Accounts > Roles management.
-
Hover over the role for which you want to set permissions and click the
 icon on the right.
icon on the right.The Edit a role pane appears.
-
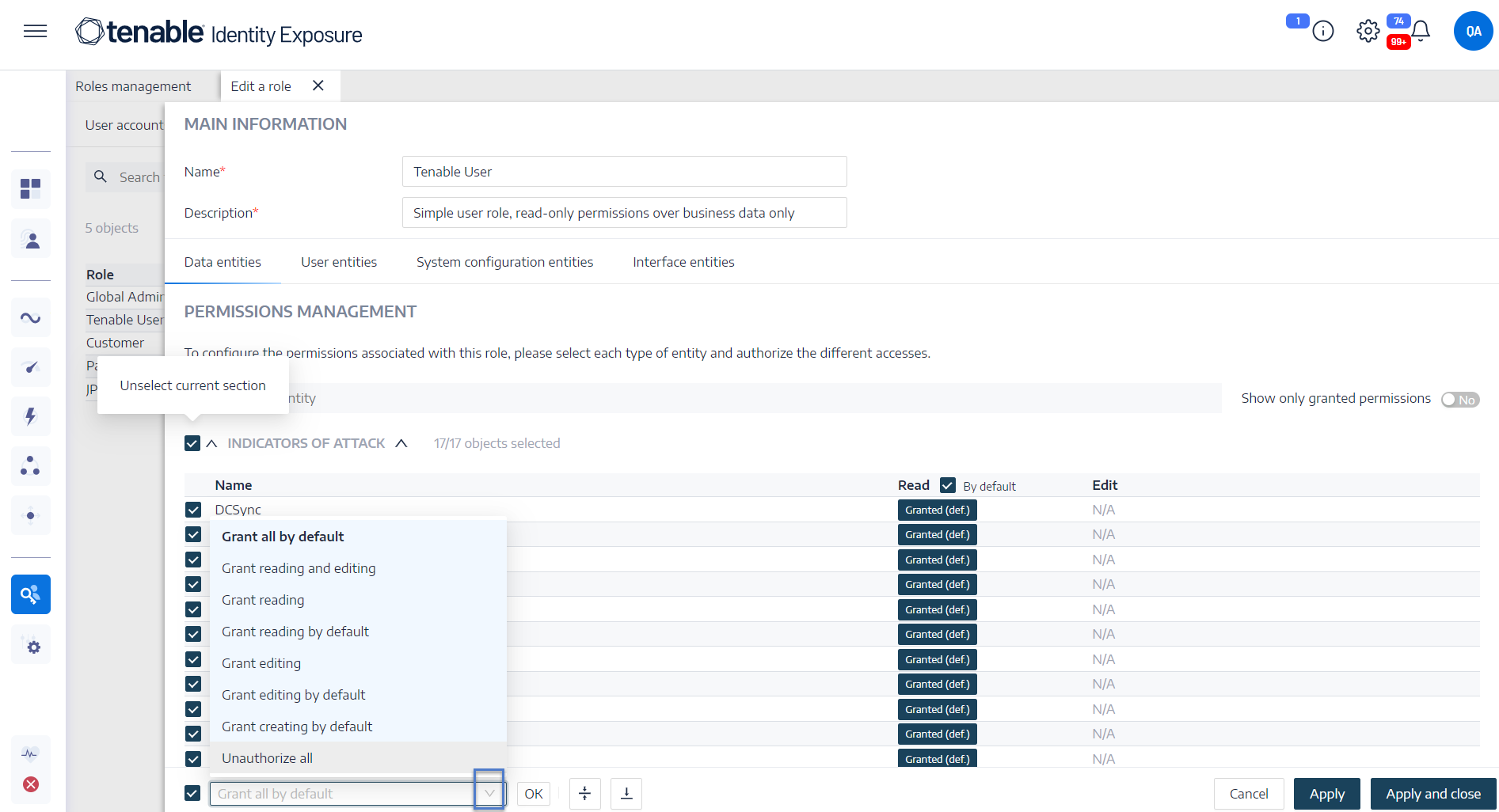
Under Permissions Management, select an entity type:
-
In the list of entity names, select the entity to set permissions on.
-
Under the columns Read, Edit, or Create, click the toggle to Granted or Unauthorized.
-
You can either:
-
Click Apply to apply the permission and keep the Edit a role pane open for further modifications.
-
Click Apply and close to apply the permission and close the Edit a role pane.
A message confirms that Tenable Identity Exposure updated the role.
-
To set permissions in bulk for a role:
-
In Tenable Identity Exposure, click Accounts > Roles management.
-
Hover over the role for which you want to set permissions and click the
 icon on the right.
icon on the right.The Edit a role pane appears.
-
Under Permissions Management, select an entity type.
-
Select the entities or section(s) of entities (for example Indicators of Exposure) to set permissions on.
-
At the bottom of the page, click the arrow on the drop-down box to display a list of permissions.
-
Select the permission(s) for the role.
-
Click OK.
A message confirms that Tenable Identity Exposure set the permissions on the entities.
Permission Types
| Permission | Description |
|---|---|
| Read | Permission to view an object or a configuration. |
| Edit |
Permission to modify an object or a configuration. Requires the Read permission to apply modifications. |
| Create |
Permission to create an object or a configuration. The Create permission requires the Read and Edit permissions to perform permitted actions on permitted resources. |
Entity Types
There are four types of entities in Tenable Identity Exposure that require permissions to access which you can tailor for each user role in your organization:
| Entity Type | Contains | Permissions | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Entities | |||
| This entity controls the permissions for setting up the monitored Active Directory and configuring the data analysis in Tenable Identity Exposure. |
|
Read, Edit, Create | |
| User Entities | |||
| This entity controls a user's ability to configure information that Tenable Identity Exposure displays for data analysis and to modify personal information and preferences. |
|
Edit, Create | |
| System Configuration Entities | |||
| This entity controls the access to the Tenable Identity Exposure platform and services. |
|
Read, Edit | |
| Interface Entities | |||
| This entity defines the permissions to access specific parts of the Tenable Identity Exposure user interface and features. | Access paths to specific Tenable Identity Exposure features. For more information, see Set Permissions on User Interface Entities (Example) | Granted, Unauthorized | |
See also