Utilizing Audit Files
SPF, DKIM, and DMARC
Sender Policy Framework (SPF) is an email authentication method which helps prevent email spoofing by checking the SPF record that is published in the domain owner's Domain Name System (DNS). SPF results are utilized by DMARC.
DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) is an authentication method which detects forged sender addresses in email. Forging signatures is a technique used in many phishing and email spam campaigns. DKIM allows the recipient to check the email signature and ensure the email came from the domain stated.
Domain Message Authentication Reporting (DMARC) is an email authentication policy and reporting protocol. DMARC builds onto SPF and DKIM protocols by adding linkage to the author (“From”) domain. This improves the protection for fraudulent email.
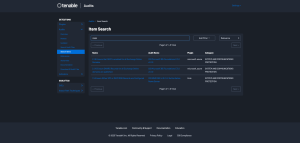
Tenable has audit files for Microsoft (CIS Microsoft 365 Foundations E3 L1 v1.5.0) that check for SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records. Additionally, an audit file (CIS BIND DNS v1.0.0 L2 Authoritative Name Server) for Unix systems, containing checks to ensure Either SPF or DKIM DNS Records are configured, is available. These audit files may be downloaded and reviewed on the Tenable Audits page. Locating audit files for key terms, such as SPF, DKIM, DMARC, and other terms should be performed on the Item Search page. Once that page is accessed type the search term, DKIM in this example, into the search bar.
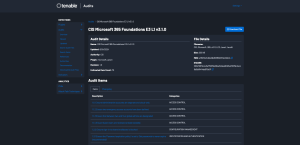
The results will be presented. From these results you can click on the Name. In this example, the first option is selected, 2.1.9 Ensure that DKIM is enabled for all Exchange Online Domains and we are presented with detailed information regarding this audit check.
Clicking on the Audit Name, in this example CIS Microsoft 365 Foundations E3 L1 v3.1.0, provides a description of the audit items, and a download button in the top right corner.
For information related to adding an audit file to Tenable Security Center, refer to the Audit File section of the Tenable documentation site.
For information related to utilizing audit files in Tenable Vulnerability Management, refer to the Compliance in Tenable Vulnerability Management Scans section of the Tenable documentation site.
For detailed information on utilizing audit files and credentialed scanning information, review the Tenable Compliance Checks Reference Guide.
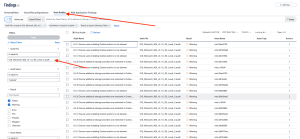
In most environments which use the Microsoft Office system, Outlook is often already the default program for email, contacts, and calendaring. Compliance checks exist to ensure group policies are set to make Outlook the default program for email. Installed web browsers and email clients which have been enumerated via software identification, can easily be searched for vulnerabilities using vulnerability text filters within the Findings sections of Tenable Vulnerability Management. The following results are available from the Host Audit section within the Findings page using filters for the audit file specified above, and filtering down to only include Outlook and either Failed or Warning audit results..
Some environments may require or benefit from the use of customized audit files. Organizations have the ability to customize. audit files and tailor audits to their specific needs. For more information on creating custom Tenable Nessus audit files, including examples, review the Example Audit Items page.