SIEM Analysis Section
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) analysis allows you to import data from SIEM providers (for example, Splunk) to evaluate events that may warrant re-scanning the affected hosts.
Note: Tenable recommends that you only use trusted self signed certs for Splunk instances that are used with Tenable Network Monitor.
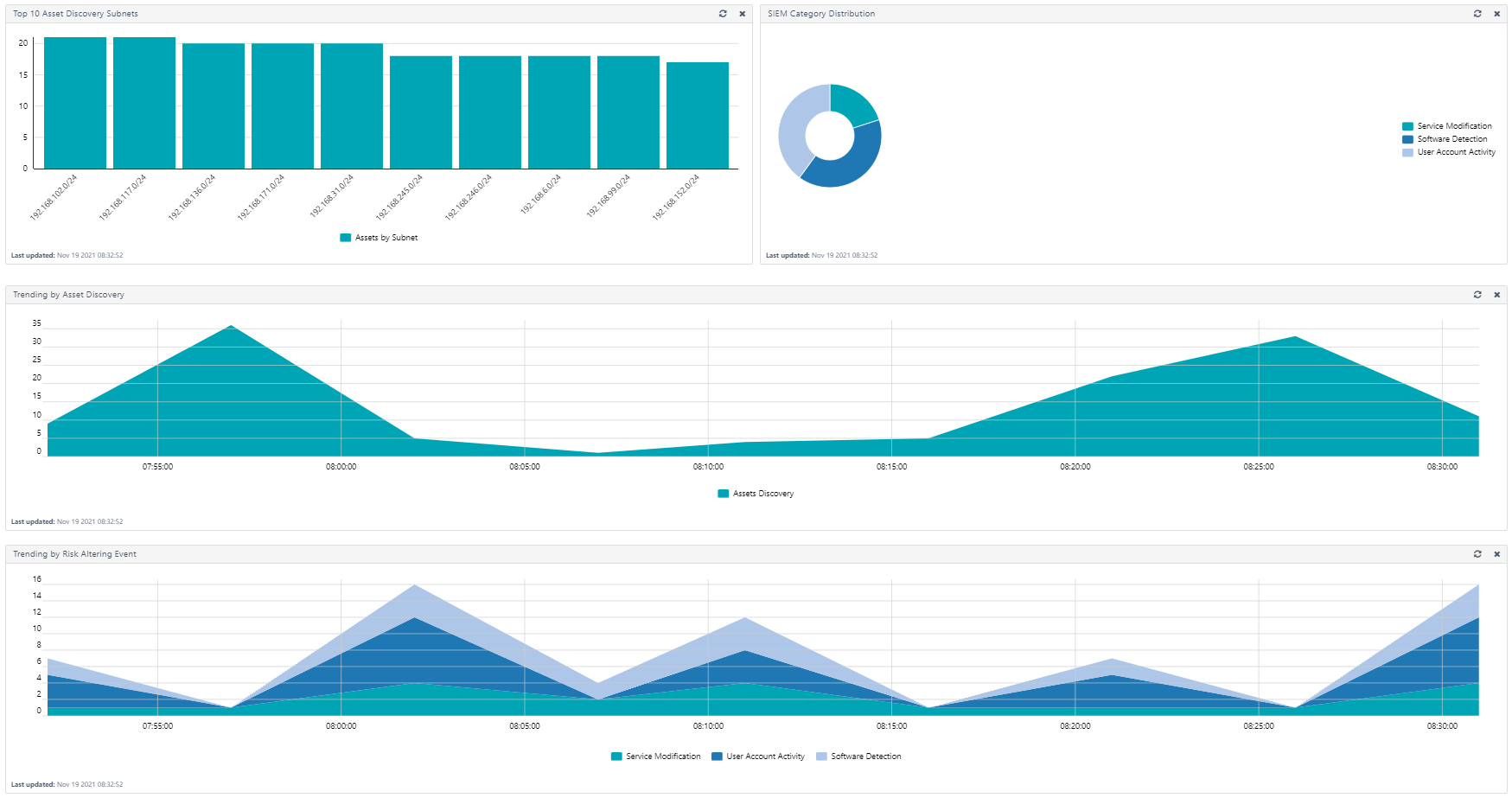
The SIEM Analysis section of the Monitoring page shows four charts that help you track and understand SIEM-related events occurring in your system:
-
Top 10 Asset Discovery Subnets
-
SIEM Category Distribution
-
Trending by Asset Discovery
-
Trending by Risk Altering Event
The SIEM Category Distribution and Trending by Risk Altering Events show data based on the risk-altering events discovered in your system. There are ![]() four risk-altering event types:
four risk-altering event types: