Example Deployment
This section demonstrates an example of NNM running on a virtual machine functioning as a NAT gateway instance within an Amazon Web Services Virtual Private Cloud (VPC).
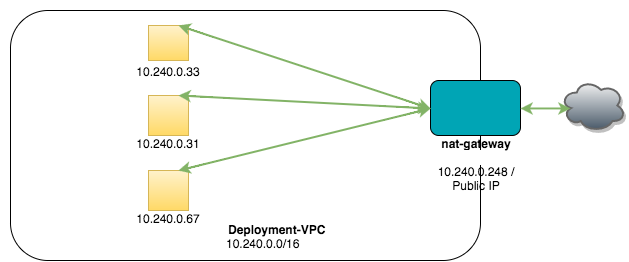
In the examples used in the instructions for setting up a NAT gateway, the VPC NNM-Deployment-VPC was created, which has the network range 10.240.0.0/16. Additionally, the virtual machine instance NNM-Deployment-NAT was created in the NNM-Deployment-Public subnet to function as the NAT gateway. In this example, three other virtual machine instances were created within the NNM-Deployment-Private subnet. None of the virtual machine instances in NNM-Deployment-Private are assigned an external IP address and all outgoing traffic is routed through NNM-Deployment-NAT.
In this example, there are four virtual machine instances within NNM-Deployment-VPC:
| VM Instance Name | Internal IP | Has External IP? |
|---|---|---|
| NNM-Deployment-NAT | 10.240.0.248 | Yes |
| example-instance | 10.240.1.33 | No |
| example-instance2 | 10.240.1.67 | No |
| example-instance3 | 10.240.1.31 | No |
NNM is running on NNM-Deployment-NAT and has the following configuration:
| Configuration Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Monitored Network Interfaces | eth0 |
| Monitored Network IP Addresses and Ranges | 10.240.0.0/16 |
With this configuration, NNM will monitor traffic
- from the internal virtual machine instances to the Internet,
- between NNM-Deployment-NAT and the internal virtual machine instances,
- from the Internet to internal virtual machine instances if you have enabled port forwarding on the NAT gateway to make them Internet accessible,
-
and between NNM-Deployment-NAT and the Internet.
Note: Due to the design of the hypervisor used by Amazon for running all virtual instances, traffic not addressed to a virtual instance can't be sniffed by the virtual instance. As a result, NNM can't monitor traffic between other virtual instances.