Key Component 3: Access Control
The focus of this key component is Access Control. The focus is on limiting access to data and services based on user roles, ensuring that individuals only have access which is required to perform job functions. This key component applies to all the following in scope devices: Boundary Firewalls, Desktop Computers, Laptops, Routers, Servers, Iaas, PaaS, and SaaS devices. Some items to focus on within this key component are:
-
Administrative privileges are tightly controlled and monitored
-
No shared accounts, every user must have their own unique account for auditing
-
Access is granted on the principles of least privilege
-
Users should have the minimum level of privileges to carry out their duties
-
-
Strong passwords must be enforced
-
Stale accounts are removed
-
User accounts should be reviewed regularly
-
-
Use multi-factor authentication (MFA)
Leveraging Tenable Security Center (formerly Tenable.sc), Tenable Vulnerability Management (formerly Tenable.io), and Tenable Identity Exposure (formerly Tenable.ad) solutions enables organizations to close attack paths, making the organization a more difficult target to attack. Tenable solutions provide organizations the data needed to identify and evaluate exposures in the environment. Tenable Identity Exposure is a fast, agent-less Active Directory security solution that helps organizations analyse their complex Active Directory environment, predict what matters most to reduce risk, and eliminate attack paths before they can be exploited.
For more detailed information on Identity and Access Management, please reference the Tenable Cyber Exposure Study: Identity and Access Management.
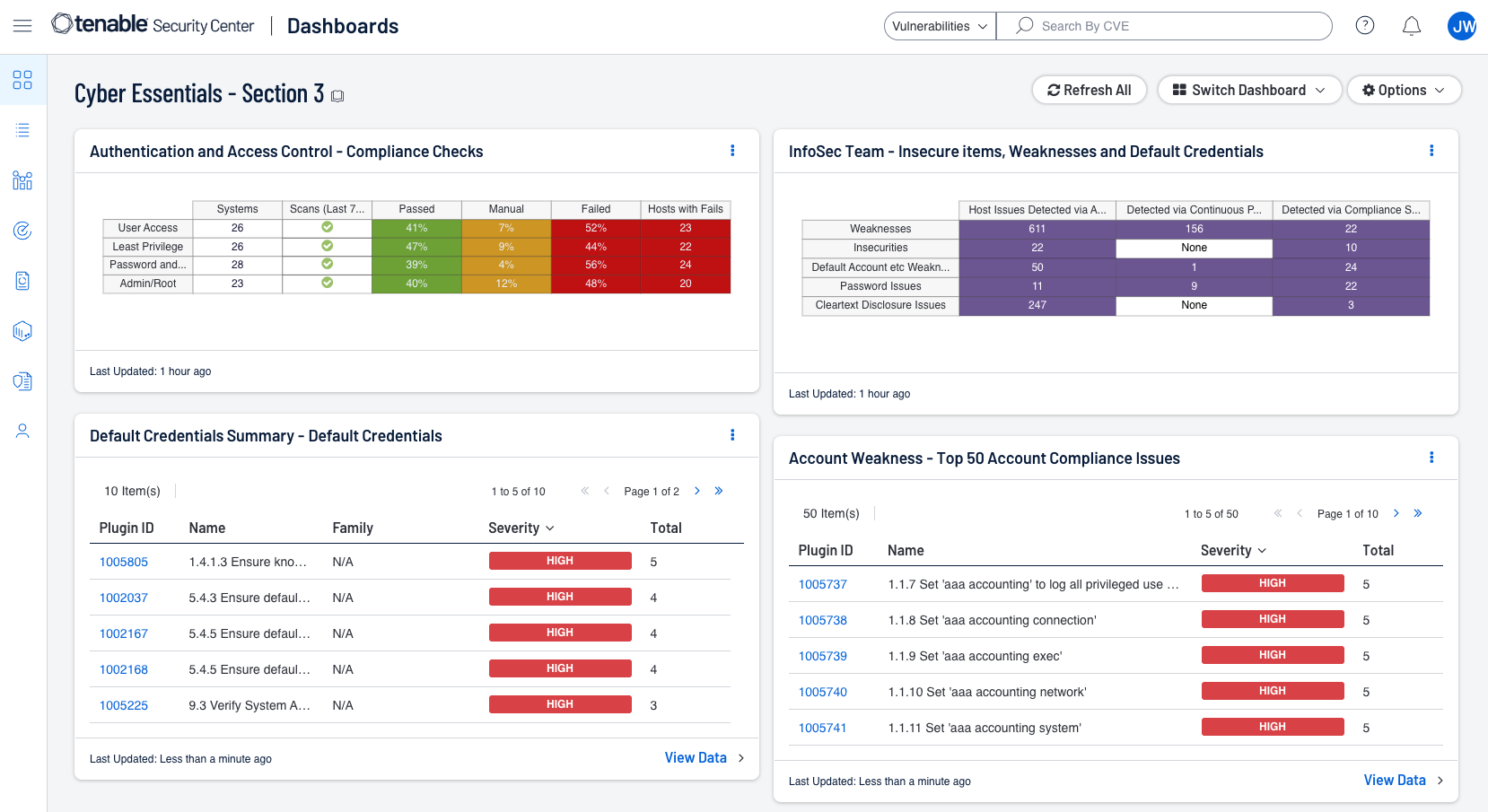
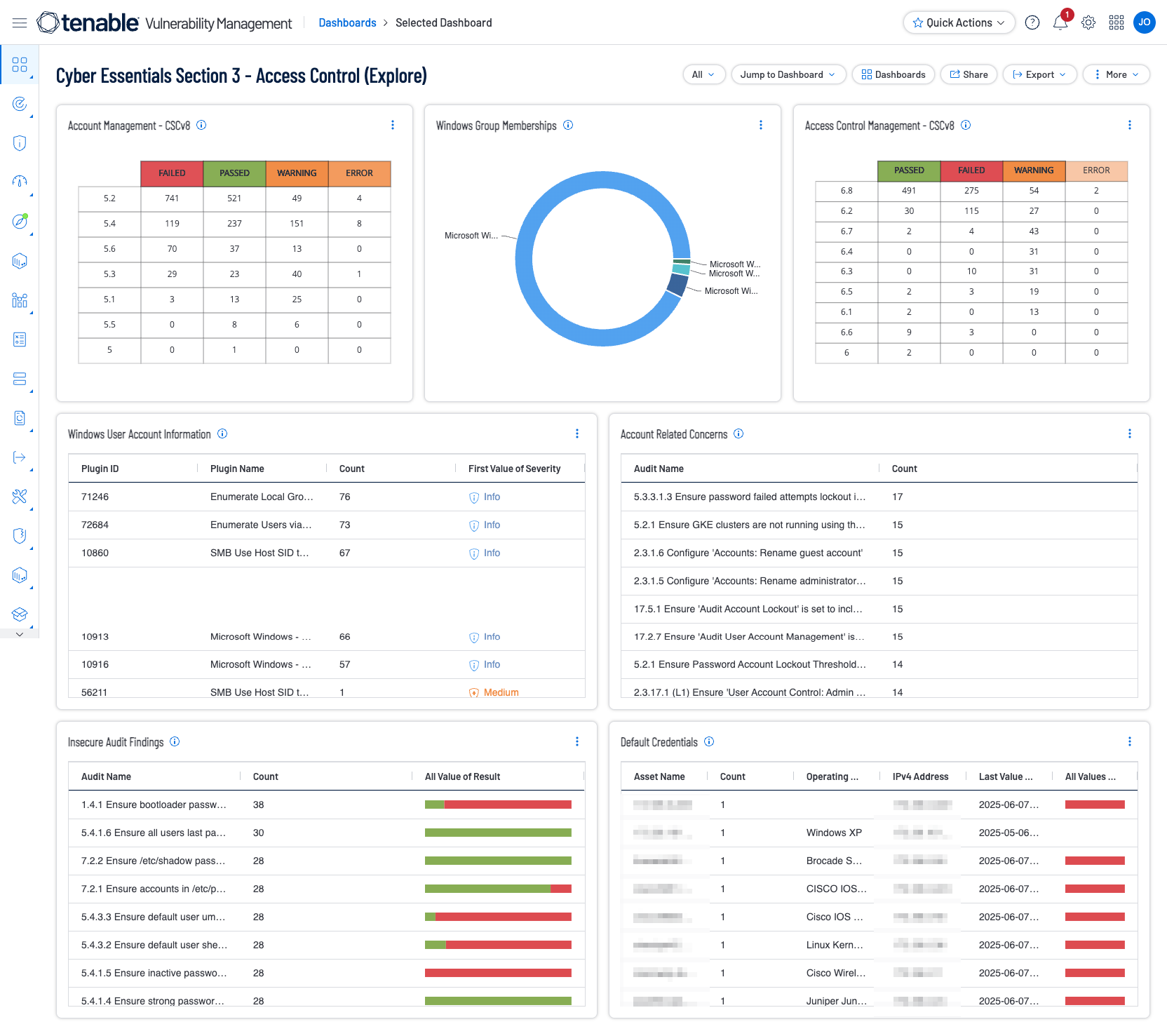
Tenable has provided a Cyber Essentials Dashboard and Report for Tenable Security Center and Tenable Vulnerability Management for this Key Component. Those dashboards and reports can be found here by using the term “Cyber Essentials” as a search query:
Security Center Dashboards and Reports
Vulnerability Management Dashboards and Reports
Shown below are screenshots of this section's dashboards for Security Center and Vulnerability Management.
The focus of the dashboards is around Access Control, and components and widgets support the goal of reducing an organisation’s risk from the most common cyber threats. The Cyber Essentials focuses on preventing high impact attacks, such as phishing, malware infection, and unauthorised access. Strong access control can limit the number of accounts which attackers can compromise, ensuring that individuals only have access which is required to perform job functions. These dashboards assist with identification of default accounts, account weakness, and account related compliance and authentication concerns.
Tenable Identity Exposure
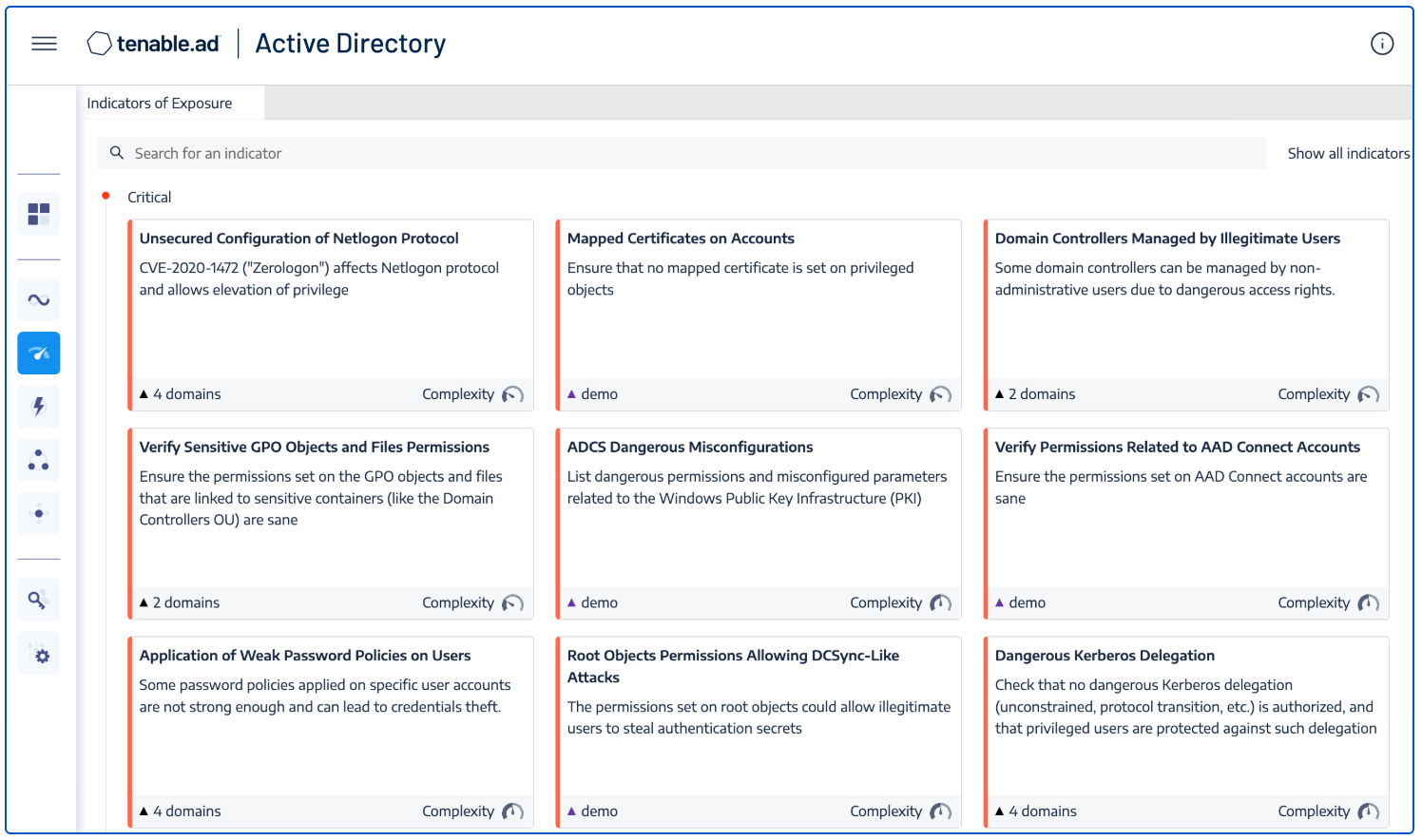
Tenable Identity Exposure provides information about an organization's Active Directory environment in an intuitive dashboard that monitors Active Directory in real-time, enabling organizations to identify at a glance the most critical vulnerabilities and recommended courses of remediation. Indicators of Exposure and Indicators of Attack discover underlying issues affecting the organization's Active Directory environment. Some of the Identity Management compliance requirements that Tenable solutions address include:
-
Identify all accounts in the environment
-
Ensure all active accounts are authorised
-
Ensure all accounts are configured to use strong authentication controls
-
Delete or disable dormant accounts
-
Restrict privileged access to only authorised users
-
Ensure group access is appropriately assigned
-
Understand configuration exposures, such as dangerous permissions
Indicators of Exposure provides an overview of critical, high, medium, and low risk exposures identified across the organization’s domains. From the landing page, security analysts can drill down for more details about which assets are exposed.
Secure Configuration Assessment Questions Directly Addressed
Questions in this section apply to: servers, desktop computers, laptops, tablets, thin clients,
mobile phones, IaaS, PaaS and SaaS. Within this section, information is provided which addresses the following questions.
A7.3. How do you ensure you have deleted, or disabled, any accounts for staff who are no longer with your organisation?
A7.8. Do you formally track which users have administrator accounts in your organisation?
A7.9. Do you review who should have administrative access on a regular basis?
A7.11. Which technical controls are used to manage the quality of your passwords within your Organisation?
Role Based Access Control
Tenable Identity Exposure provides various methods to access the information collected through the Indicators of Exposure (IoE) and Indicators of Attack (IoA) panes. Tenable Vulnerability Management provides the ability to use the Explore Findings through the use of dashboards and reports.
The first step in taking control of the organization’s Identity Management is to enumerate every user account in the environment and determine the level of access the account is granted. All user accounts must be uniquely identified and assigned to particular entities, such as users and applications.
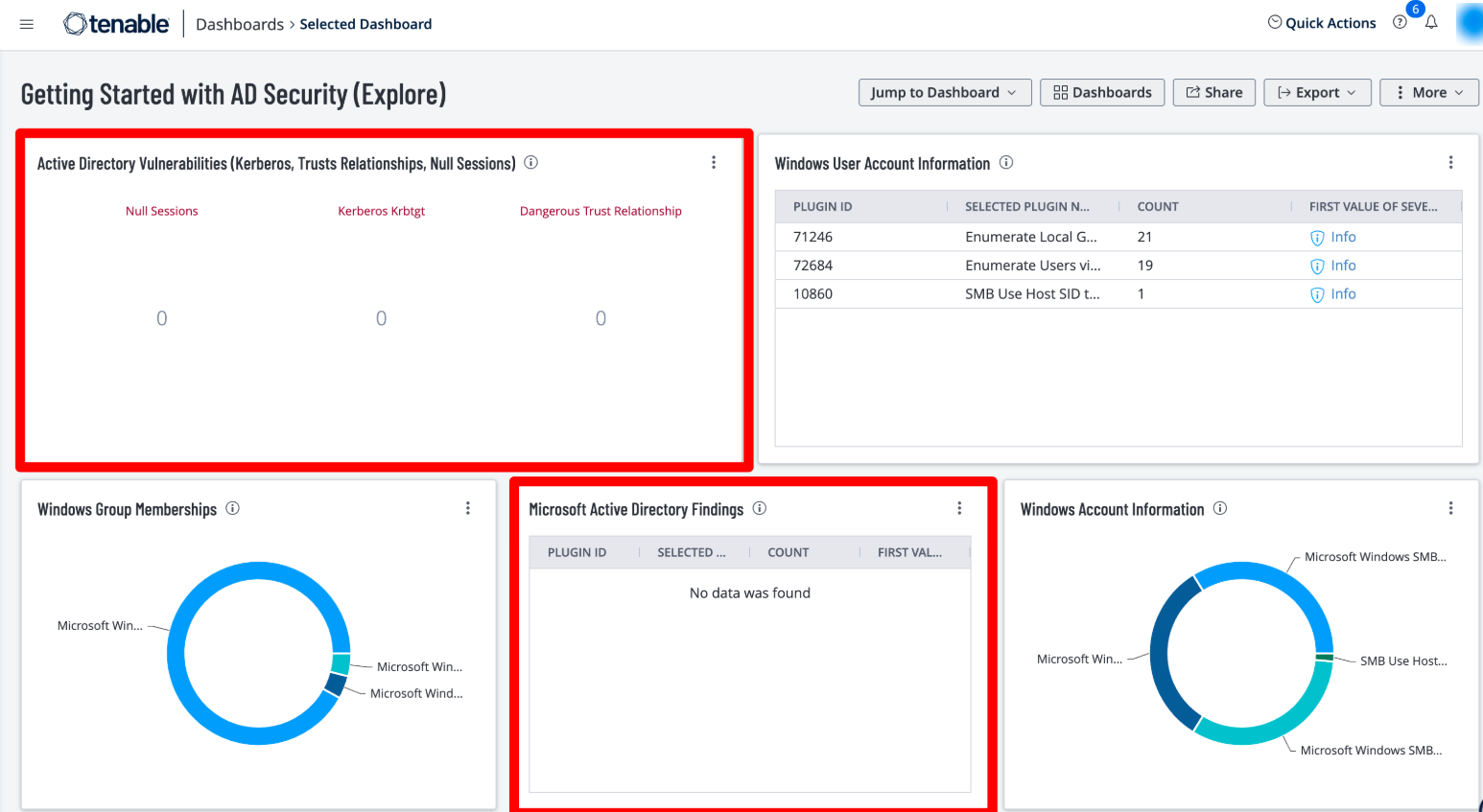
The Getting Started with AD Security dashboard in Tenable Vulnerability Management contains the following widgets to enumerate user accounts:
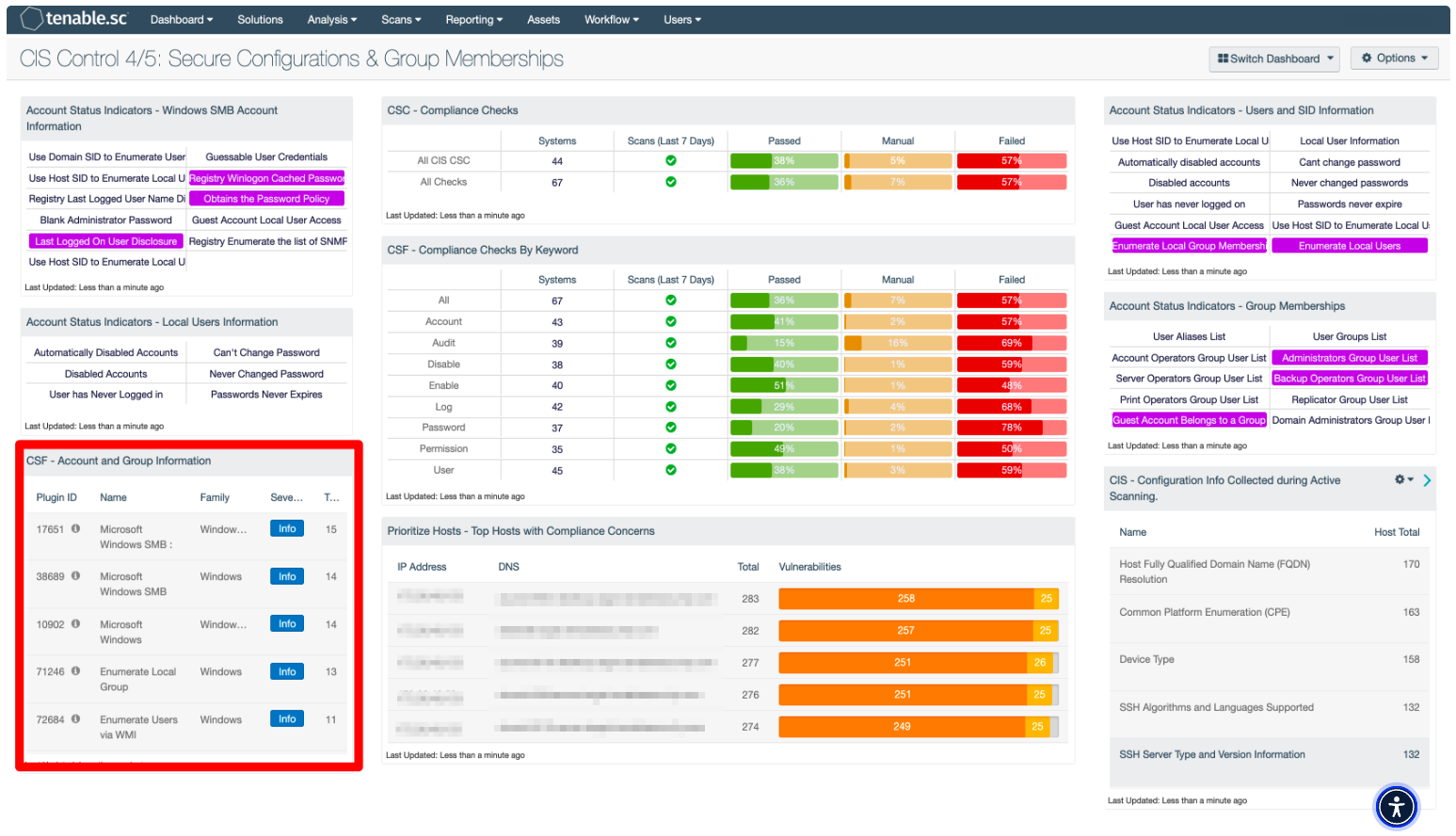
Windows User Account Information – This widget displays counts for user accounts and security identifiers (SID). Plugins report on potential user account vulnerabilities such as disabled accounts, accounts that have never logged in, accounts with passwords that have never changed, and more.
Windows Group Memberships – This widget displays information for Windows default groups such as administrators, server operators, account operators, backup operators, print operators, and replicator groups.
Windows Account Information – This widget displays counts related to Microsoft Windows SMB plugins that focus on user account information. Plugins focus on vulnerabilities such as SMB blank administrator passwords, SMB password policies, guest accounts, cached passwords, and more.
Organizations can use the CSF - Account and Group Information widget located in the CIS Control 4/5: Secure Configurations & Group Memberships dashboard in Tenable Security Center, which leverages plugins that enumerate Windows account information.
Users and Groups
While Active Directory is typically used by most organizations, there are many other accounts for non-Windows platforms that must be identified. Tenable Nessus contains a number of plugins and plugin families that help organizations enumerate users and groups on the network. The Windows: User management plugin family contains nearly 30 plugins that enumerate Microsoft Windows users and groups. Other useful Nessus plugins for user and group enumeration include:
-
10894 Microsoft Windows Users Group List – This plugin uses the supplied credentials to retrieve the list of groups each user belongs to. Groups are stored for further checks.
-
126527 Microsoft Windows SAM user enumeration – This plugin enumerates domain users on the remote Windows system using Security Account Manager.
-
95928 Linux User List Enumeration – This plugin enumerates local users and groups on the remote host.
-
95929 macOS and Mac OS X User List Enumeration – This plugin extracts the member lists of ‘Admin’ and ‘Wheel’ groups on the remote host.
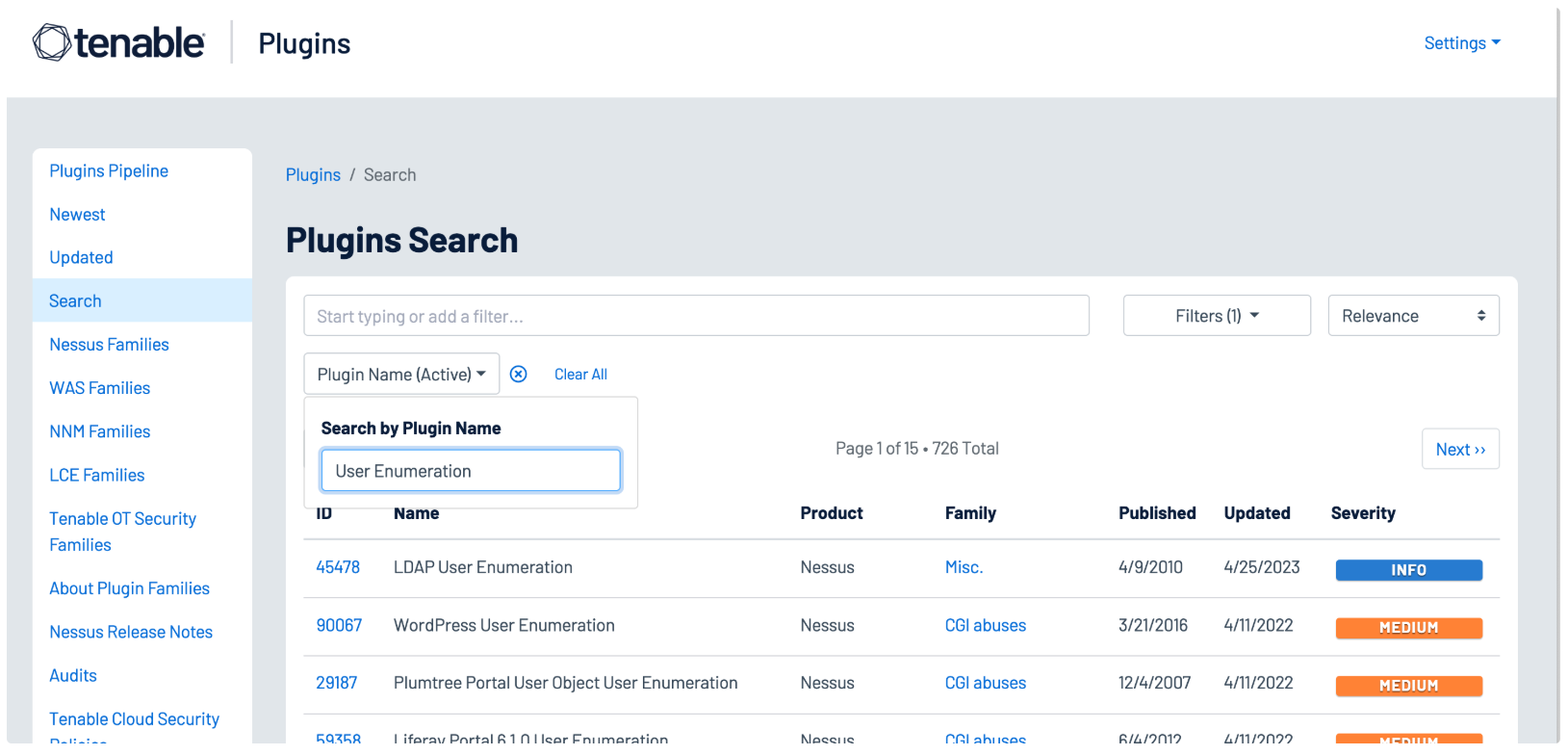
A number of other Nessus plugins that contain the key words “User Enumeration” in a plugin name search using the Plugin Name filter identify WordPress, VMware, LDAP, and other software applications that maintain user accounts, as shown in the following image:
Active Directory accounts can be configured to escape global password renewal policies. Accounts set up in this manner can be used indefinitely without ever changing their password. Tenable recommends reviewing user and administrator accounts to ensure they are not configured to have this attribute.
The following Indicators of Exposure (IoE) in Tenable Identity Exposure can be used to identify issues with user accounts in an organization’s Active Directory environment:
-
Accounts with Never Expiring Passwords
-
Application of Weak Password Policies on Users
-
Dangerous Kerberos Delegation
-
Account that Might Have an Empty Password
-
AdminCount Attribute Set on Standard Users
-
User Account Using Old Password
-
Kerberos Configuration on User Account
Privileged Accounts
Most compliance standards and frameworks require privileged users to have a non-privileged account for standard user activities, such as web browsing or reading emails. Tenable Nessus and Tenable Identity Exposure provide the tools to identify settings for root and admin accounts.
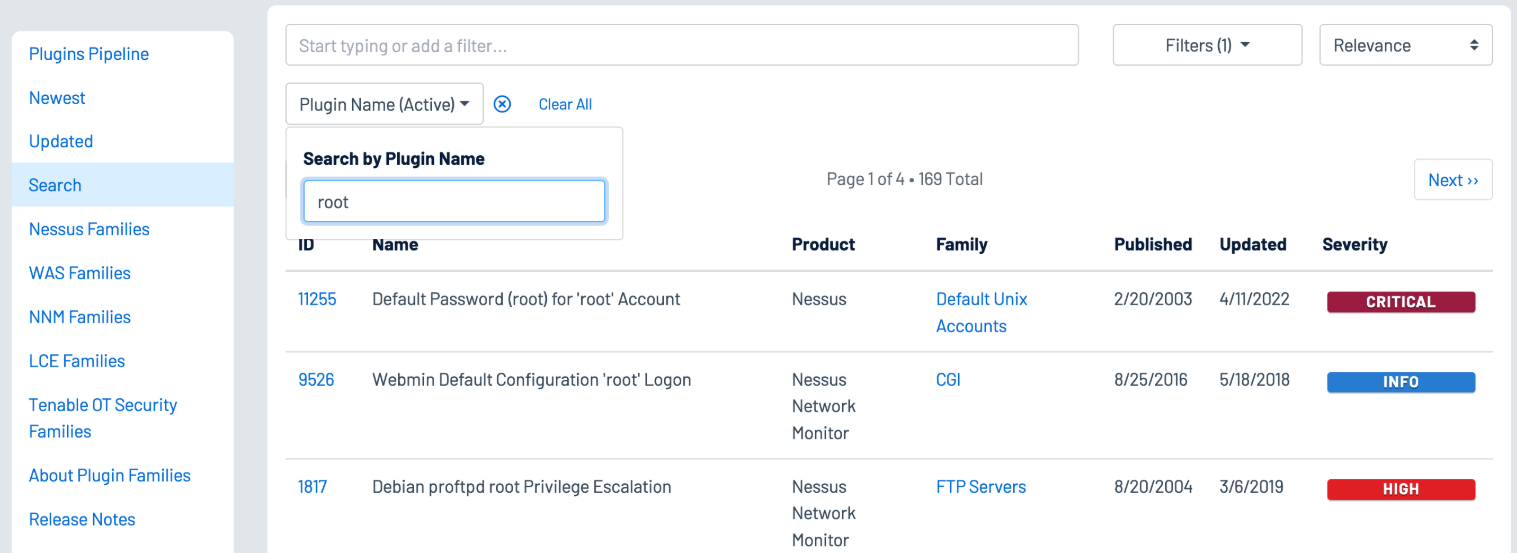
Using the Plugin Name filter on the Plugins Search page enables analysts to search for plugins with terms that identify privileged accounts such as “root,” “admin,” or “privileged,” as shown below:
The following Indicators of Exposure (IoE) in Tenable Identity Exposure can be used to identify Active Directory settings for privileged accounts:
-
Mapped Certificates on Accounts
-
Ensure SDProp Consistency
-
Native Administrative Group Members
-
Privileged Accounts Running Kerberos Services
-
Potential Clear-Text Password
-
Protected Users Group not Used
-
Logon Restrictions for Privileged Users
-
Local Administrative Account Overview Management
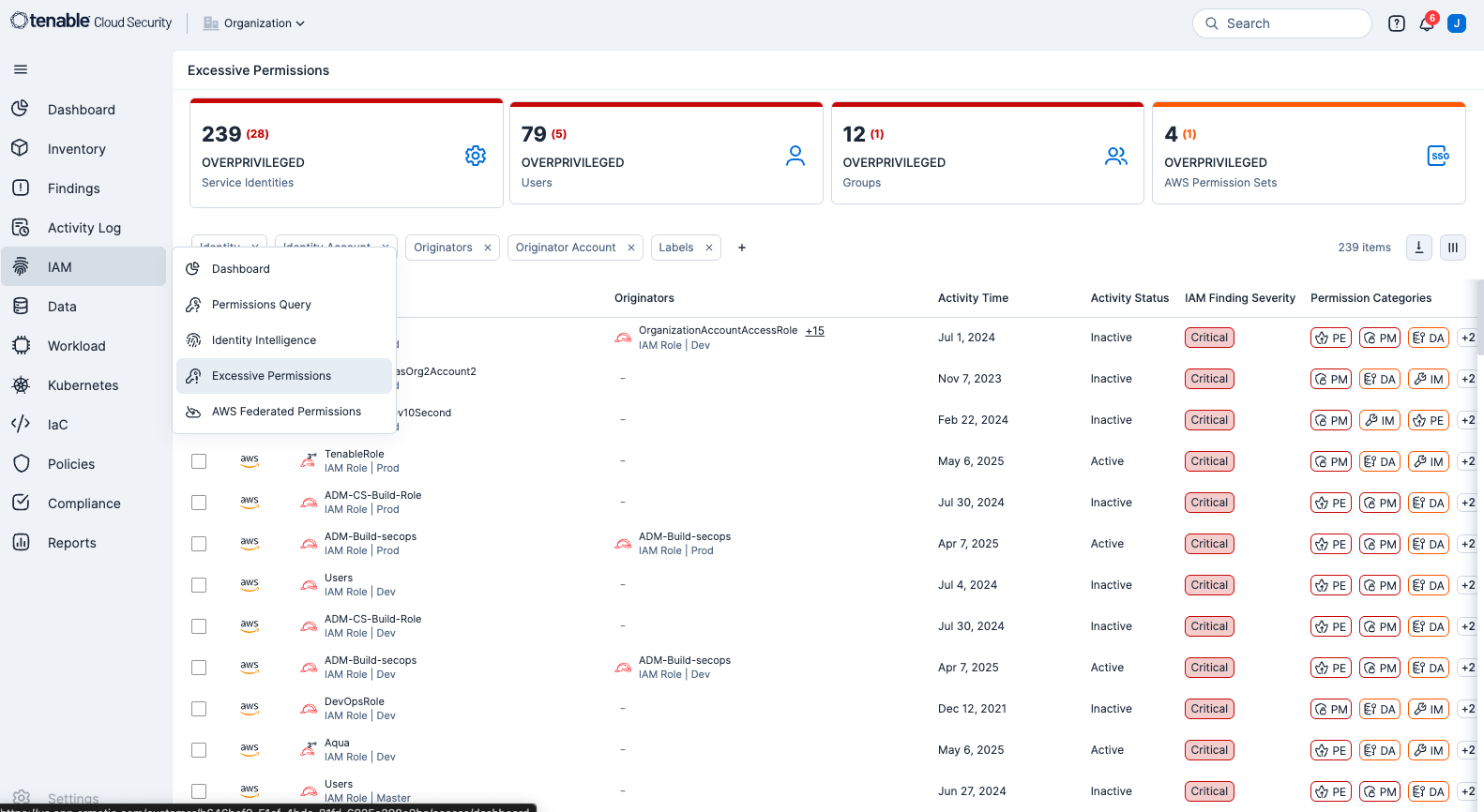
Tenable Cloud Security has the ability to display Excessive Permission with a single click. Drilling down into any of the results will provide an overview, details, recommendations, and remediation steps to fix the issues.
Disable Inactive and Default Accounts
Operating Systems and applications are often distributed with service and default accounts that are either not password-protected or have a default password that is well-known. Tenable Nessus and Tenable Identity Exposure help identify these accounts, enabling organizations to review and disable any unnecessary accounts to reduce the attack surface. Organizations can leverage the following Nessus plugins to enumerate service and default accounts:
-
Plugin Family: Default Unix Accounts – This plugin family contains over 170 Nessus plugins that check for the existence of default accounts/passwords on a number of devices. In addition, there are many plugins that check for simple passwords such as “0000”, “1234”, and more commonly identified password combinations for “root” or administrator accounts.
-
171959 Windows Enumerate Accounts – This plugin enumerates all Windows Accounts
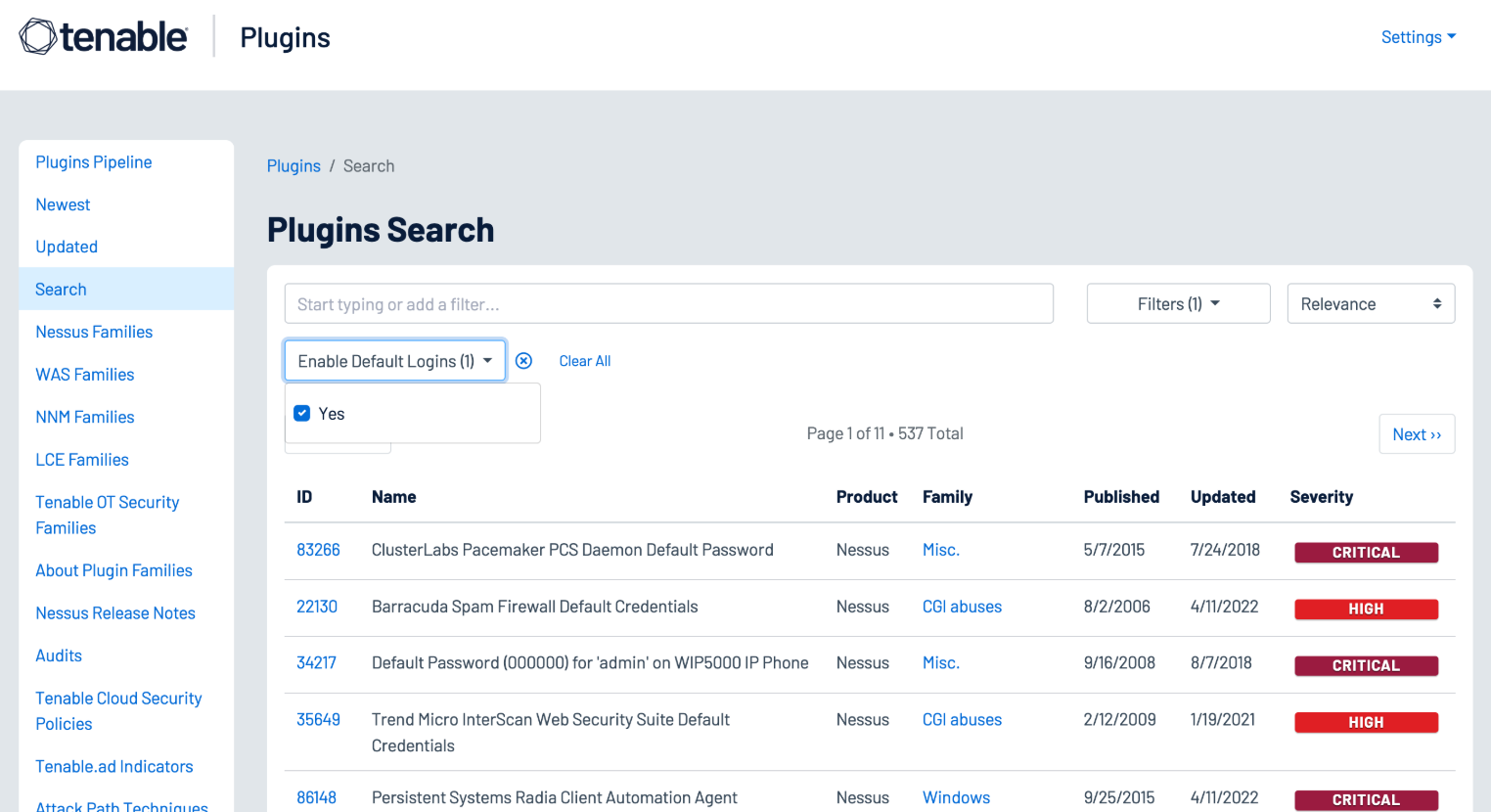
Several hundred plugins can be identified by searching for “Default Account” from the Nessus Plugins Search page using the Enable Default Logins filter. Nessus default account plugins are available for Databases, Web Servers, SCADA devices, Unix/Linux devices, Cisco devices and more. Many of the plugins are associated with the Default Unix Account Nessus family, however, many are in other families as well.
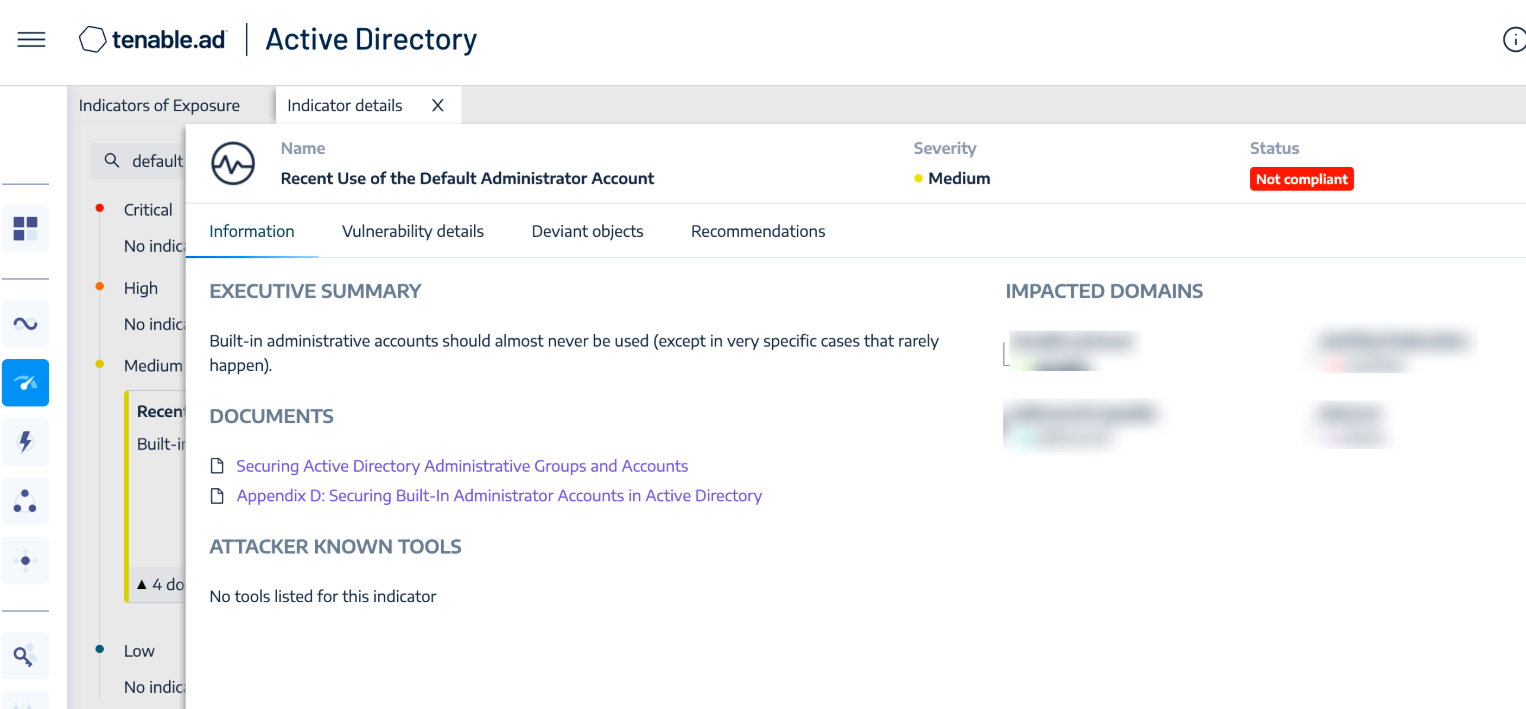
In addition, Tenable Identity Exposure provides the ability to determine if a default administrator account was recently used in the environment, as shown in the image below:
MFA
Within this section, information is provided which addresses the following questions.
A7.14. Do all of your cloud services have multi-factor authentication (MFA) available as part of the service?
A7.16. Has MFA been applied to all administrators of your cloud services?
A7.17. Has MFA been applied to all users of your cloud services?
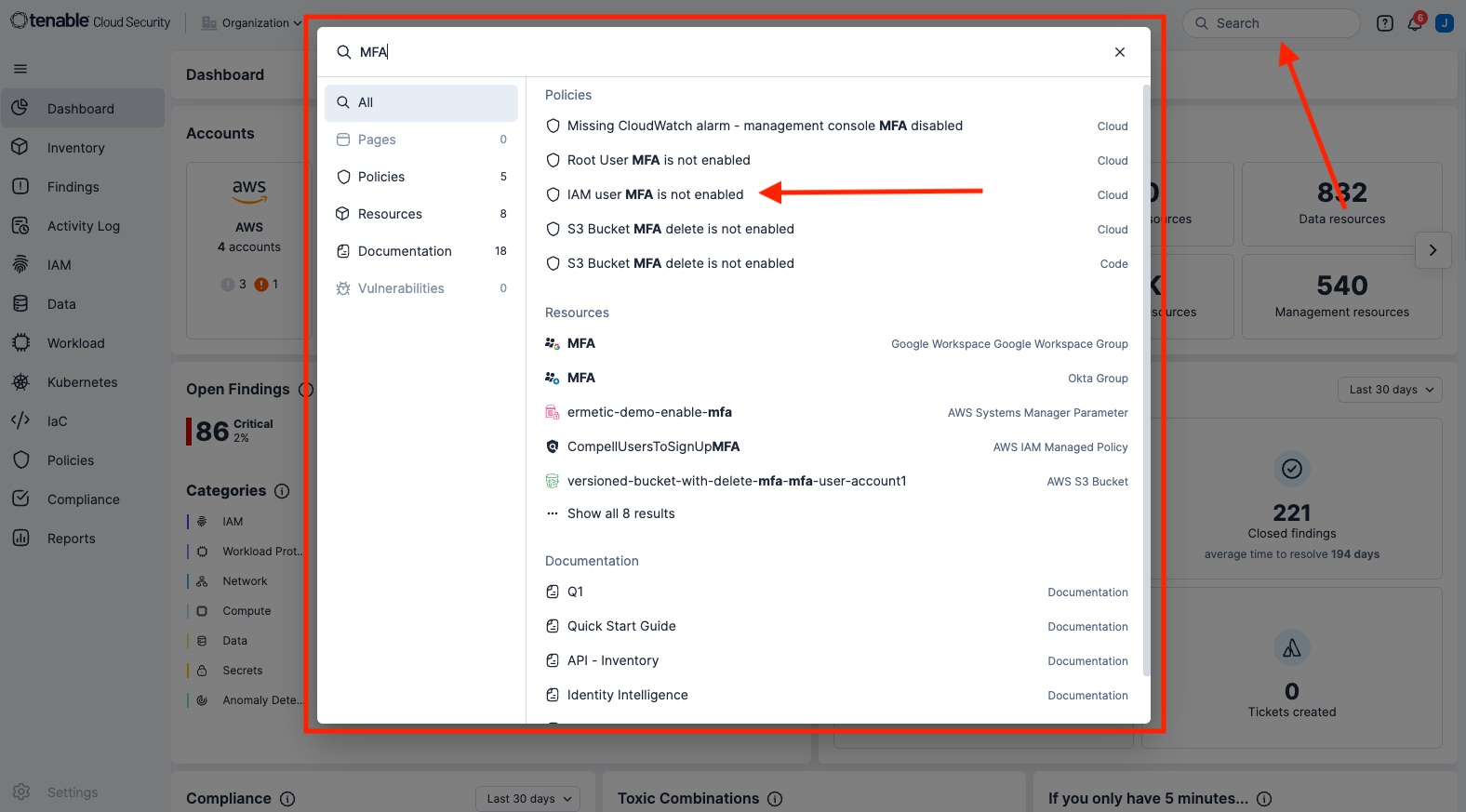
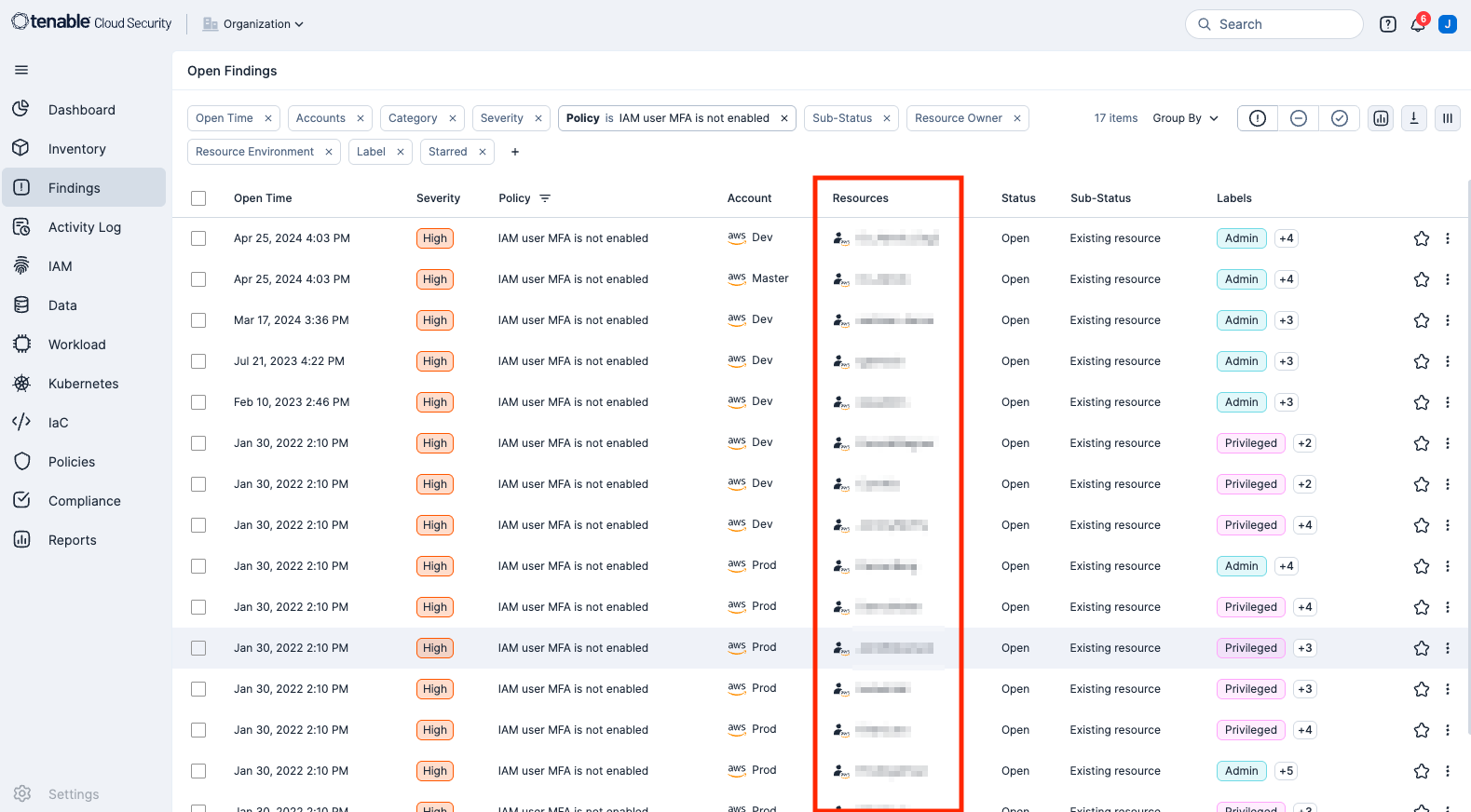
Within Tenable Cloud Security, key search terms can be entered into the search bar in the top right corner. For this example, entering MFA returns the following search results, displayed below. From these search results “IAM user MFA is not enabled” will be selected.
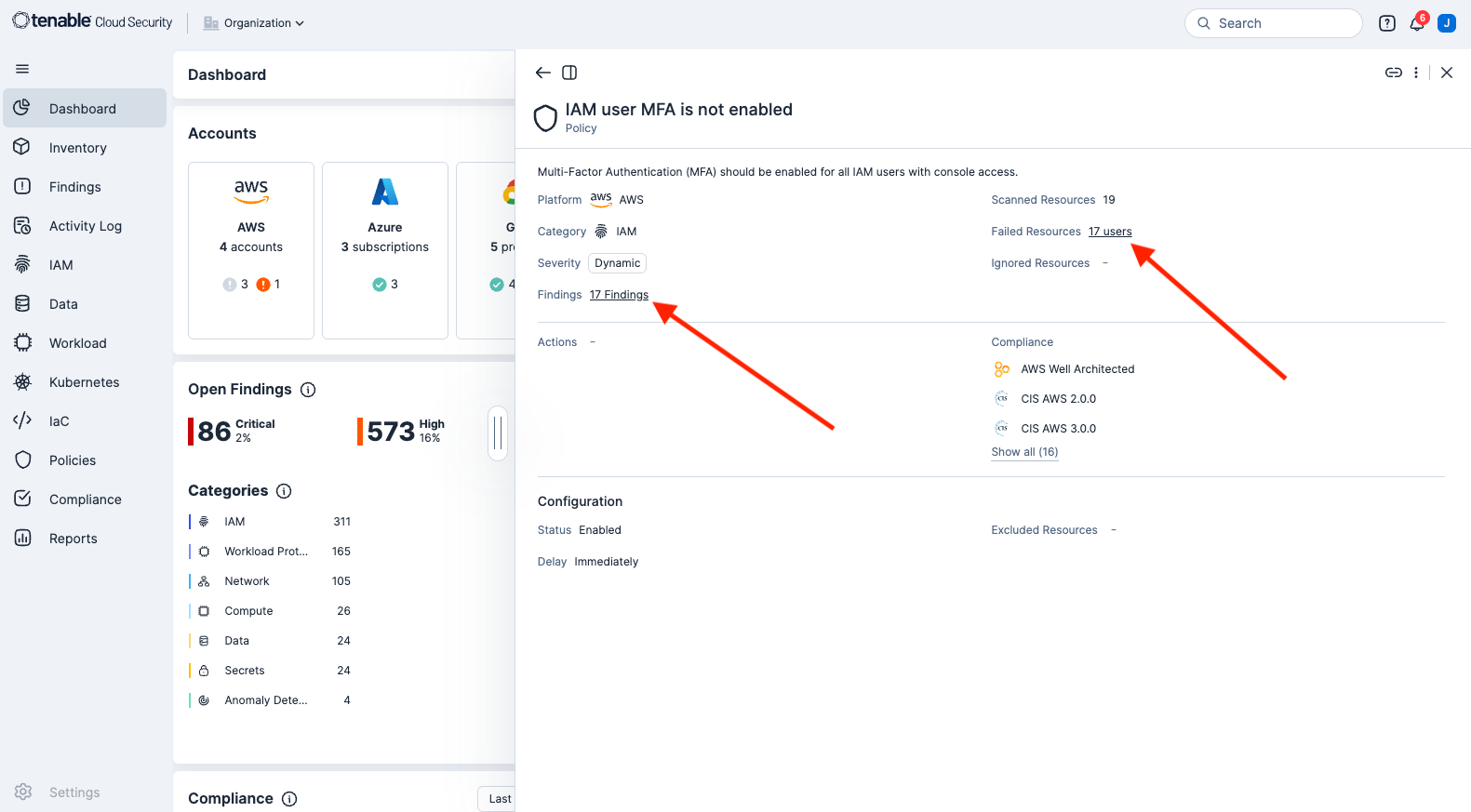
A new window will be opened displaying a summary of the findings. To view the users with no MFA enabled, clicking the Failed Resources link will open a pop up with only a user listing. For more detail, select the Findings link.
The Findings page is then displayed with additional information, including a column displaying each user that does not have MFA enabled (usernames pixelated for public release in this document. Normally, all usernames are clearly visible). From here analysts can continue to drill down and gather additional information on the Open Findings page.