2-2: Identity and Access Management
For domain 2-2, The National Cybersecurity Authority states:
“To ensure secure and restricted logical access to OT/ICS assets in order to prevent unauthorized access and allow only authorized access for users, which are necessary to accomplish assigned tasks."
Leveraging Tenable Security Center, Tenable Vulnerability Management, and Tenable Identity Exposure solutions enables organizations to close attack paths, making the organization a more difficult target to attack. Tenable solutions provide organizations the data needed to identify and evaluate exposures in the environment. Tenable Identity Exposure is a fast, agentless Active Directory security solution that helps organizations analyze their complex Active Directory environment, predict what matters most to reduce risk, and eliminate attack paths before they can be exploited.
As well as expanding on ECC 2-2-3, the Identity and Access Management control in the OTCC requires the OT/ICS access management lifecycle to be separated and independent from IT. The control further talks about how certain types of accounts should be handled (e.g., service accounts, default accounts, privileged accounts, etc.).
Users and Groups
While Active Directory is typically used by most organizations, there are many other accounts for non-Windows platforms that must be identified. Tenable Nessus contains a number of plugins and plugin families that help organizations enumerate users and groups on the network. The Windows: User management plugin family contains nearly 30 plugins that enumerate Microsoft Windows users and groups. Other useful Nessus plugins for user and group enumeration include:
-
10894 Microsoft Windows Users Group List – This plugin uses the supplied credentials to retrieve the list of groups each user belongs to. Groups are stored for further checks.
-
126527 Microsoft Windows SAM user enumeration – This plugin enumerates domain users on the remote Windows system using Security Account Manager.
-
95928 Linux User List Enumeration – This plugin enumerates local users and groups on the remote host.
-
95929 macOS and Mac OS X User List Enumeration – This plugin extracts the member lists of ‘Admin’ and ‘Wheel’ groups on the remote host.
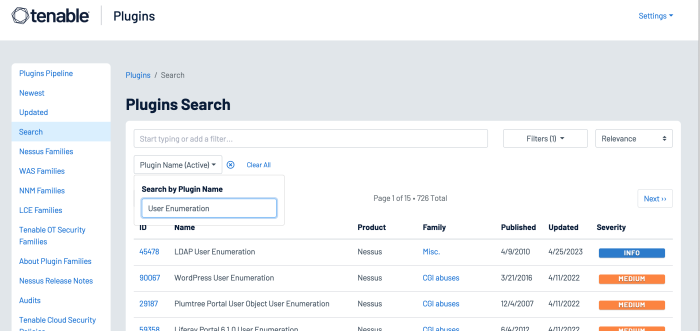
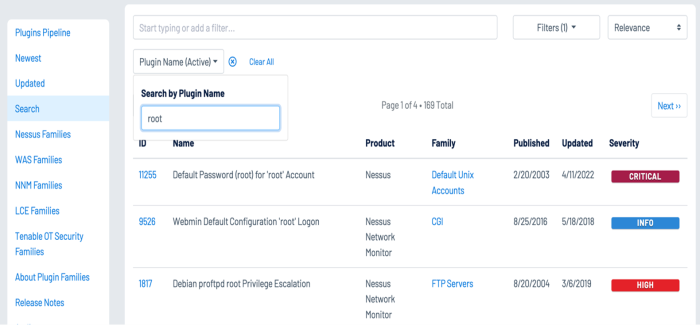
A number of other Nessus plugins that contain the key words “User Enumeration” can be found in the Plugin Name search using the Plugin Name filter, identify WordPress, VMware, LDAP, and other software applications that maintain user accounts:
Service and Default Accounts
Operating Systems and applications are often distributed with service and default accounts that are either not password-protected, or have a default password that is well known. Tenable Nessus and Tenable Identity Exposure help identify these accounts, enabling organizations to review and disable any unnecessary accounts to reduce the attack surface. Organizations can leverage the following Nessus plugins to enumerate service and default accounts:
-
Plugin Family: Default Unix Accounts – This plugin family contains over 170 Nessus plugins that check for the existence of default accounts/passwords on a number of devices. In addition, there are many plugins that check for simple passwords such as “0000,” “1234,” and more commonly identified password combinations for “root” or administrator accounts.
-
171959 Windows Enumerate Accounts – This plugin enumerates all Windows Accounts
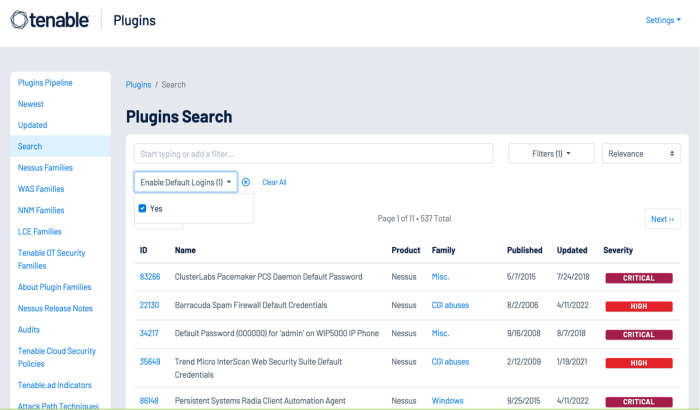
Several hundred plugins can be identified by searching for “Default Account” from the Nessus Plugins Search page using the Enable Default Logins filter. Nessus default account plugins are available for Databases, Web Servers, SCADA devices, Unix/Linux devices, Cisco devices and more. Many of the plugins are associated with the Default Unix Account Nessus family, however, many are in other families as well.
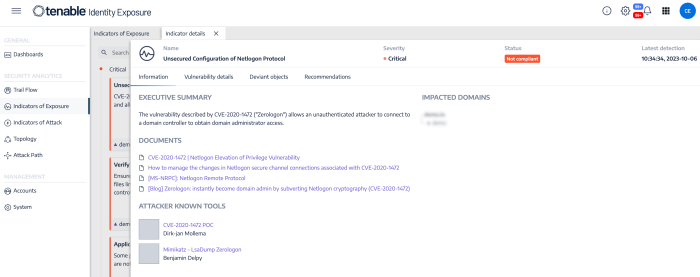
In addition, Tenable Identity Exposure provides the ability to determine if a default administrator account was recently used in the environment:
User Access Controls
Strong authentication mechanisms help validate that accounts are being used by the authorized user to read, create, modify, or delete data in accordance with business needs. The Center for Internet Security (CIS) provides benchmarks for a large number of Operating System platforms and applications. Tenable Research writes audit files for these benchmarks to help organizations quickly determine their alignment with the CIS recommendations. The benchmarks include guidance on access controls for both non-privileged and privileged accounts.
User Accounts
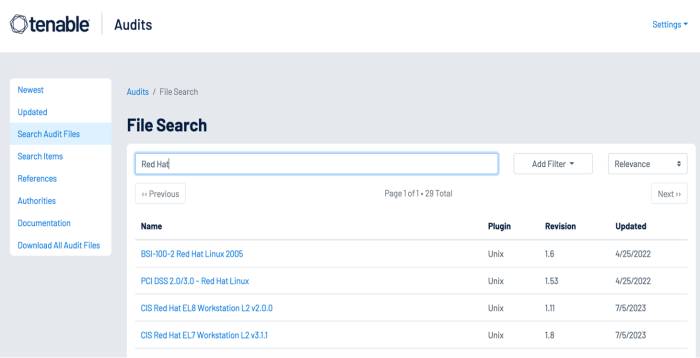
Non-privileged user accounts require strong access controls to prevent attackers from gaining local access to the network. Attackers often target user accounts to exploit weaknesses in the local network and escalate privileges. Security teams can use the Tenable Audits Search page to find audit files for their Operating System platforms, which check for common compliance requirements such as “Lock Workstations after Inactivity” and other issues.
Active Directory accounts can be configured to escape global password renewal policies. Accounts set up in this manner can be used indefinitely without ever changing their password. Tenable recommends reviewing user and administrator accounts to ensure they are not configured to have this attribute.
The following Indicators of Exposure (IoE) in Tenable Identity Exposure can be used to identify issues with user accounts in an organization’s Active Directory environment:
-
Accounts with Never Expiring Passwords
-
Application of Weak Password Policies on Users
-
Dangerous Kerberos Delegation
-
Account that Might Have an Empty Password
-
AdminCount Attribute Set on Standard Users
-
User Account Using Old Password
-
Kerberos Configuration on User Account
Privileged Accounts
Most compliance standards and frameworks require privileged users to have a non-privileged account for standard user activities, such as web browsing or reading emails. Tenable Nessus and Tenable Identity Exposure provide the tools to identify settings for root and admin accounts.
Using the Plugin Name filter on the Plugins Search page enables analysts to search for plugins with terms that identify privileged accounts such as “root,” “admin,” or “privileged.”
The following Indicators of Exposure (IoE) in Tenable Identity Exposure can be used to identify Active Directory settings for privileged accounts:
-
Mapped Certificates on Accounts
-
Ensure SDProp Consistency
-
Native Administrative Group Members
-
Privileged Accounts Running Kerberos Services
-
Potential Clear-Text Password
-
Protected Users Group not Used
-
Logon Restrictions for Privileged Users
-
Local Administrative Account Overview Management
Dormant Accounts
User accounts that have not been accessed in more than a year provide an opportunity for attackers to leverage compromised credentials and perform brute-force attacks. Nessus plugins 10915 or 10899 Microsoft Windows - Local Users Information: User Has Never Logged In displays a list of Windows accounts where the user has never logged in. The Sleeping Accounts Indicator of Exposure in Tenable Identity Exposure detects accounts that have not been accessed in over a year.
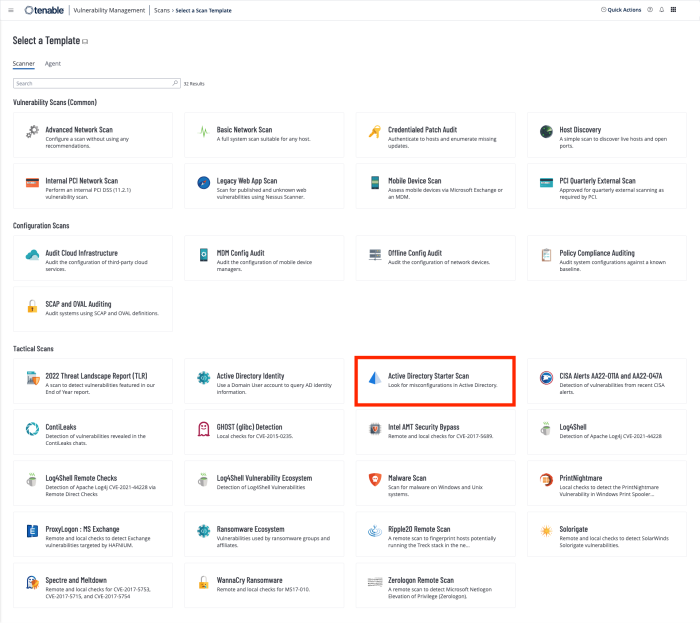
The Active Directory Starter Scan Template contains 10 hygiene checks that attackers often exploit while seeking to navigate their targets' Active Directory. These plugins focus on the most common attack paths, such as guessing or cracking accounts’ secrets, impersonating other users, privilege escalation and lateral across domains.
Maintenance
Every structure – physical or virtual – requires maintenance to maintain structural integrity over time. Even the most hardened infrastructure is subject to degradation with regular use. Tenable Security Center, Tenable Vulnerability Management, and Tenable Identity Exposure provide comprehensive monitoring to detect drift from the desired state.
Administrator and user activity can degrade security controls over time if the system is not maintained properly. Regular scanning of the environment using the Nessus audit files identifies drift in security controls.
The following Indicators of Exposure (IoE) in Tenable Identity Exposure can be used to identify maintenance issues in Active Directory:
-
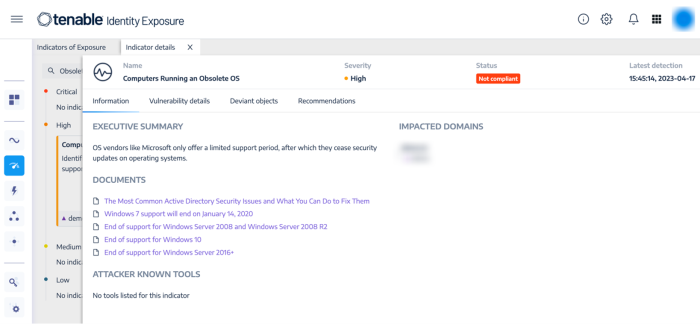
Computers Running an Obsolete OS (High)
-
Disabled Accounts in Privileged Groups (Low)
-
Unlinked, Disabled, or Orphan GPO (Low)
Step 1: From the Indicators of Exposure tab in Identity Management, search for the above listed IoEs in the search field:

Step 2: Click on one of the displayed tiles to drill down into more details:
Using the Indicators of Exposure within Tenable Identity Exposure assists the organization in reviewing user access rights; something that must be done periodically (ECC 2-2-3-5) and in response to cybersecurity incidents, personnel roles changes or whenever there is a change in OT/ICS system architecture (OTCC 2-2-1-10).
For organizations where an on-premises solution is required Tenable Security Center is able to provide coverage along with an on-premises installation of Tenable Identity Exposure. An installation guide for Tenable Identity Exposure can be seen here. Utilizing the Getting Started with AD Security dashboard (see figure 9), Tenable Security Center unifies security data from across the organization, providing a comprehensive view and understanding of the organization's overall security posture. Using a diverse deployment of Nessus scanners, administrators have complete visibility into network-connected assets with comprehensive vulnerability assessment coverage. When Active Directory concerns are identified, Tenable Security Center quickly provides alerts via workflows and notifications, which speed up incident response and vulnerability remediation. Additionally, Tenable.ad provides a comprehensive cyber exposure determination of Active Directory hosts.